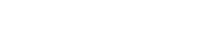5 Major Forces That Drive the Forex Market

Forex trading has a long and glorious history, dating back to the Middle Ages. But at that time, no one could have predicted how enormous this market could become in the future. Today, the forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily turnover of $6.6 trillion. It operates 24 hours a day and comprises over 170 different currencies.
Even Covid-19 could not hamper its dominant march. While the global stock markets experienced their worst decline since the Great Depression, during the 2020 pandemic, the story was very different for forex. During the pandemic, interest in forex trading saw a significant rise, with an approximately 300% increase in forex trading volumes between March and June 2020.
The growth was more prominent in developing regions, such as South East Asia, Eastern Europe and Africa. This period might have been volatile, but it is this volatility that offered multiple trading opportunities for traders of all levels of skill and experience. As Sun Tzu once famously said, “In the midst of chaos, there is also opportunity.” But to take advantage of these opportunities, you first need to know the factors that move the forex market. So, here are 5 major forces that drive prices in this market.
1. Interest Rates
Interest rates are arguably the biggest factor to influence the forex market. Benchmark interest rates are decided by the central banks of different countries, such as the US Federal Reserve, Bank of England, the European Central Bank and the Reserve Bank of Australia. But how does it impact the forex market? Interest rates impact the capital flow between different countries. If the interest rates in one country are high and are expected to increase further in the future, it makes investing in instruments such as fixed income securities of that country more attractive. This causes increased foreign investment inflow, which boosts the demand for the local currency. With a higher demand, the value of the currency appreciates with respect to other currencies.
Similarly, lower interest rates can trigger an outflow of capital from the country. This can lead to a depreciation in the value of the domestic currency. However, during the Covid-19 pandemic, central banks across the world have been keeping interest rates low to bolster their economies, allowing businesses and individuals to access cheaper loans.
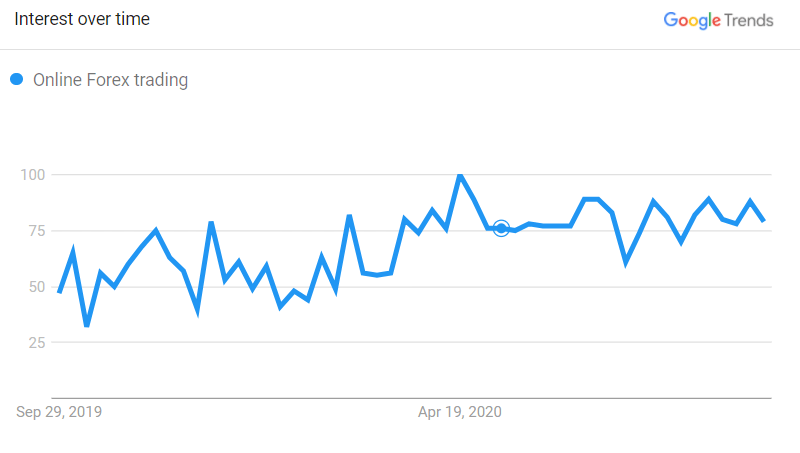
2. Inflation
Currency exchange rates are also affected by changes in inflation rate. A country with a lower inflation rate, compared to another nation, would experience a comparative appreciation in its currency value. Conversely, a country with a higher inflation rate is likely to witness a depreciation in its currency value. This is because with inflation, the amount of goods and services that can be bought with the domestic currency declines. In other words, inflation makes your money less valuable. Stable economies, such as the US, tend to have lower interest rates.
On the other hand, extremely low inflation rates or deflation is not great for forex as well. Such situations discourage consumer spending. The prices may be low, but people expect them to fall further in future. This is detrimental for the economy.
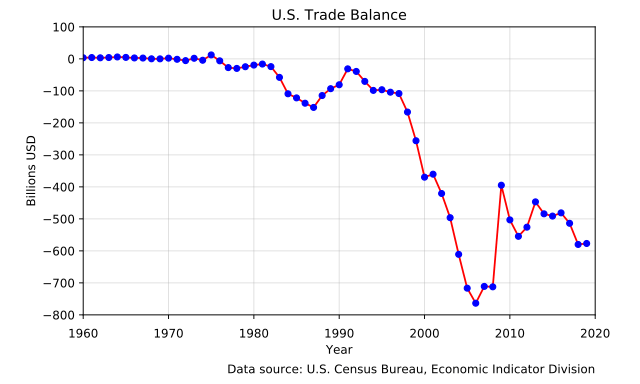
3. Trade Balance
Trade balance is the difference between the value of exports and imports of a country. A positive trade balance helps the domestic currency value appreciate. This is because positive trade balance means that there is high demand for the goods and services of the country, which means that capital is flowing into the nation. Similarly, if the country is importing more than it is exporting, there would be a trade deficit. This would lead to the domestic currency’s value declining.
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=75343607
But there are certain exceptions to this, the most notable one being the United States. The US has been in a trade deficit since the mid-1970s. But the value of the US dollar has not depreciated each year. This is due to the greenback’s reserve currency status. It helps keep the demand for the US dollar high. This is one of the reasons why the USD is considered a safe haven investment by many traders.
4. Geopolitical Conditions
The political stability of a country would have a positive impact on its currency value. Stable nations attract more foreign investment. This increases the demand for the local currency, helping the domestic currency’s value appreciate. On the other hand, political instability, protests and civil wars can send the value of the domestic currency tumbling.
Political relations between countries also affect the forex market. For instance, the deteriorating relations between the US and China sparked off a trade war. By July 2018, tariffs worth $34 billion were imposed by the US on Chinese imports. To remain price competitive, China started devaluing the Yuan. China also imposed tariffs on imports from America. The trade war impacted other countries as well, with Thailand and New Zeeland weakening their currencies to cope with the impact of the trade war on the supply chains. Similarly, Brexit also had a major impact on currencies, especially the Great British Pound.
5. National Debt
Also known as public debt, sovereign debt or public interest, this is the debt owed by a country’s central government. When the government collections in taxes are lower than the spending, the government often resorts to debt to fill the gap. This creates a perception that the government is not fiscally responsible and that the nation might have an unstable economy. This, in turn, attracts lower foreign investment, reducing the value of the domestic currency. Similarly, if there is low debt, the local currency gains in value, since investors gain confidence in the government.
The pandemic has led to increased market volatility. The remainder of 2020 is likely to see high volatility as well, given the impending US presidential election. During such times, robust analysis of market moving factors and appropriate risk management measures are crucial for satisfying trading experiences.