FX Carry Trading for Beginners

Interest rate hikes by major central banks throughout 2022 triggered a resurgence in forex carry trading. This forex trading strategy involves trading currency pairs strategically to capitalise on the difference in interest rates between the two countries to which the currencies belong.
Carry Trading
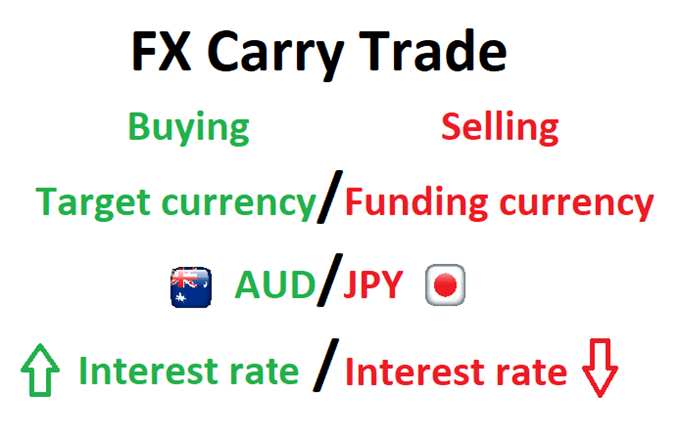
The simplest way to understand carry trading involves buying a high-yielding currency, or a currency of a country with high interest rates, by funding it with a low-yielding one. With this strategy, traders take advantage of interest rate differentials.
https://a.c-dn.net/b/2NFLqr/currency-carry-trade_body_FX-carry-trade-infographic.png
Interest rates in a country fluctuate because of central bank decisions. Central banks hike interest rates to curtail money supply, which has a dampening effect on inflation. Conversely, they reduce interest rates to stimulate growth during a recession.
Carry traders need to consider not only interest rate differentials but also the appreciation potential of the currency pair. This is because when the interest rate in a country increases, foreign investors rush in to purchase the currency, driving its valuation higher. Traders aim to enter at the beginning of the tightening cycle and remain long on the currency till the interest rate differentials remain profitable.
Traders stay abreast of the news for any possibilities of rate cuts by the central bank. When traders believe the central bank is gearing up for a rate cut, they exit the currency.
Carry Trade Examples
The greatest example of carry trading is the AUD/JPY forex pair during 2002 to 2007. The Reserve Bank of Australia hiked interest rates to 4.5%, while the Bank of Japan maintained them at 0%. This gave traders a window of opportunity to the dual advantage of appreciation in the currency pair and benefits of the large interest rate difference between the Australian dollar and the Japanese yen. The low borrowing cost of the yen have been leveraged by commodity and equity traders as well. During these years, carry traders shorted the yen to buy US and Chinese stocks.
In February 2023, the Hong Kong dollar attracted shorters as its valuation declined against the greenback and traders sold the currency to buy high-yielding assets in the US.
Factors to Consider While Choosing a Currency Pair for Carry Trading
Taking successful positions in carry trading requires:
Significant Interest Rate Differentials: The first step to plan a carry trade is to identify two countries with a large interest spread. This ensures that traders can still book profits from interest revenue even if the currency pair does not move even a pip.
The Direction of Movement of the Currency Being Purchased: Experienced traders seek to buy high-yield currencies on an upward trajectory.
Volatility in the High-Yielding Currency: A currency pair with a large interest rate differential and low volatility is preferable to one with a small yield difference and high volatility.
How Do Traders Earn Interest?
Let’s assume that a trader has taken a long position on currency X, purchasing it with currency Y. The long position continues for N days.
Daily Interest = [IR(X) – IR(Y)] * NV / N
Here NV is the currency pair’s notional value (exchange rate).
Carry Trading With Leverage
Using even 2%-5% leverage and there being only a modest difference in interest rates, a trader can potentially earn substantial gains. This is because a 2% leverage translates to 20 times the carry profit. However, traders must use leverage cautiously, as this can also amplify potential losses. Risk management becomes essential in such scenarios.
Carry Trading Versus Arbitrage
While carry trading involves taking advantage of interest rate differentials, arbitrage involves taking advantage of the exchange difference of a currency pair in two different markets. Arbitrage is possible because of temporary market inefficiencies and is a short-term trading strategy. Conversely, carry trading is a relatively long-term strategy. It relies on taking advantage of distinct monetary policies across countries according to their economic conditions.
Carry Trading Strategy for Beginners
Here are the steps beginner traders can use to build their carry trading strategy:
- Identify a low- and a high-yielding currency. When doing this, novice traders may consider staying away from emerging economies. Even though these economies tend to have much higher interest rates, the high volatility of their currencies and limited potential for appreciation, makes carry trading riskier and less profitable. For instance, currencies like the South African rand or Turkish lira are more susceptible to devaluation against major currencies like the euro or US dollar.
- Trade with a broker that offers competitive swap rates and leverage. This optimises your purchase and profit potential.
- Use technical indicators to confirm the positive direction of your carry trade. This means that the high-yielding currency should also have a higher probability of appreciation. Depreciation or stagnancy in the funding currency can be useful too.
The most popular carry trading FX pairs are:
USD/CHF
USD/JPY
CAD/CHF
NZD/CHF
Risks Associated with Carry Trading
Since the forex market is exceptionally volatile, traders always have to account for some exchange rate uncertainty before making trading decisions.
If the interest rate declines in the investing currency and the funding currency appreciates, traders may end up making lower profits or even losses from the trade. This makes risk management key for carry trading.
Risk Management in Carry Trading
For hedging carry trades, traders may use CFD-based forex trading. CFDs allow traders to hedge fluctuations in currency prices. Using the 200-day moving averages is one of the most common ways of hedging carry trades.
To Sum Up
- Carry trading is an FX strategy that takes advantage of interest rate differentials between two currencies.
- It involves borrowing a currency with low-interest rates and using it to buy one that yields high interests.
- Ideally, for a successful carry trade, interest rate differentials should remain constant with a slight appreciation in the currency pair.
- Traders can hedge their carry trades with CFDs.
- Risks include fluctuations in exchange rates and a reduction in interest rates.
Disclaimer:
All data, information and materials are published and provided “as is” solely for informational purposes only, and is not intended nor should be considered, in any way, as investment advice, recommendations, and/or suggestions for performing any actions with financial instruments. The information and opinions presented do not take into account any particular individual’s investment objectives, financial situation or needs, and hence does not constitute as an advice or a recommendation with respect to any investment product. All investors should seek advice from certified financial advisors based on their unique situation before making any investment decisions in accordance to their personal risk appetite. Blackwell Global endeavours to ensure that the information provided is complete and correct, but make no representation as to the actuality, accuracy or completeness of the information. Information, data and opinions may change without notice and Blackwell Global is not obliged to update on the changes. The opinions and views expressed are solely those of the authors and analysts and do not necessarily represent that of Blackwell Global or its management, shareholders, and affiliates. Any projections or views of the market provided may not prove to be accurate. Past performance is not necessarily an indicative of future performance. Blackwell Global assumes no liability for any loss arising directly or indirectly from use of or reliance on such information herein contained. Reproduction of this information, in whole or in part, is not permitted.